By Klaus D. Linse
Delta sleep inducing peptide, or DSIP, is a nonapeptide with the sequence WAGGDASGE and a molecular weight of 849 dalton. The peptide was discovered by G. Schoeneberger and M. Monnier in 1974. Results from different research groups indicated that DSIP plays an important role in stress-resistance since DSIP showed stress-protective, antiseizure, and immunomodulating effects. Furthermore, it has been found to also play a role in slowing down the aging process. The peptide mainly induces delta-sleep in rabbits, rats, mice, and humans. However, in cats, the effect on REM sleep was found to be more pronounced. Using radio immune assays (RIA) and immunohistochemistry it was possible for researchers to localize DSIP-like material in the brain and in peripheral organs of the rat as well as in the plasma of several mammals. In addition, the peptide has also been observed to affect electrophysiological activity, neurotransmitter levels in the brain, circadian and locomotor patterns, hormonal levels, psychological performance, and the activity of neuro-pharmacological drugs including their withdrawal. DSIP influences the nocturnal rise of N-acetyltransferase (NAT) activity in the rat pineal gland. The peptide is now known to have multifunctional regulatory properties and numerous studies have confirmed its stress-protective and adaptive activity. Apparently the exact biochemical origin of this peptide is not well known, however, in humans, the sequence is present in the Jumonji domain-containing protein 1B or JMJD1B protein, in lysine-specific demethylase 3B, and the KIAA1082 protein as can be revealed by a BLAST search of the human genome. The JMJD1B protein, encoded by JMJD1B gene, is a ubiquitous protein demethylase that specifically demethylates Lys-9 of histone H3. The protein appears to play a central role in histone regulation. The demethylation of Lys residue generates formaldehyde and succinate. In addition this protein may have tumor suppressor activity. The KIAA1082 protein belongs to a protein domain family that is part of the cupin metallo-enzyme superfamily, smart00558, which includes a JmjC domain encoded by the KIAA1082 gene. This neuropeptide when infused into the mesodiencephalic ventricle of recipient rabbits induces spindle and delta electro-encephalography (EEG) activity and reduced motor activities. Electroencephalography (EEG) refers to the recording of electrical activity along the scalp and measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current flows within the neurons of the brain.
Delta sleep inducing peptide, or DSIP, is a nonapeptide with the sequence WAGGDASGE and a molecular weight of 849 dalton. The peptide was discovered by G. Schoeneberger and M. Monnier in 1974. Results from different research groups indicated that DSIP plays an important role in stress-resistance since DSIP showed stress-protective, antiseizure, and immunomodulating effects. Furthermore, it has been found to also play a role in slowing down the aging process. The peptide mainly induces delta-sleep in rabbits, rats, mice, and humans. However, in cats, the effect on REM sleep was found to be more pronounced. Using radio immune assays (RIA) and immunohistochemistry it was possible for researchers to localize DSIP-like material in the brain and in peripheral organs of the rat as well as in the plasma of several mammals. In addition, the peptide has also been observed to affect electrophysiological activity, neurotransmitter levels in the brain, circadian and locomotor patterns, hormonal levels, psychological performance, and the activity of neuro-pharmacological drugs including their withdrawal. DSIP influences the nocturnal rise of N-acetyltransferase (NAT) activity in the rat pineal gland. The peptide is now known to have multifunctional regulatory properties and numerous studies have confirmed its stress-protective and adaptive activity. Apparently the exact biochemical origin of this peptide is not well known, however, in humans, the sequence is present in the Jumonji domain-containing protein 1B or JMJD1B protein, in lysine-specific demethylase 3B, and the KIAA1082 protein as can be revealed by a BLAST search of the human genome. The JMJD1B protein, encoded by JMJD1B gene, is a ubiquitous protein demethylase that specifically demethylates Lys-9 of histone H3. The protein appears to play a central role in histone regulation. The demethylation of Lys residue generates formaldehyde and succinate. In addition this protein may have tumor suppressor activity. The KIAA1082 protein belongs to a protein domain family that is part of the cupin metallo-enzyme superfamily, smart00558, which includes a JmjC domain encoded by the KIAA1082 gene. This neuropeptide when infused into the mesodiencephalic ventricle of recipient rabbits induces spindle and delta electro-encephalography (EEG) activity and reduced motor activities. Electroencephalography (EEG) refers to the recording of electrical activity along the scalp and measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current flows within the neurons of the brain.
Another peptide called “delta sleep-inducing immunoreactive peptide (DIP)” is a 77-residue NH2-terminally acetylated peptide that was originally isolated from porcine brain (pDIP) using polyclonal antibodies against the delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP). As reported by Seidel et al in 1997 pDIP was detected via DSIP-specific antibodies. It is thought that these antibodies may have recognized the sequence GGDA in DSIP and GGSA in pDIP. However the peptide is otherwise not sequence-related to this supposed sleep-inducing peptide. The pDIP sequence contains a putative leucine-zipper motif, a Pro/Glu rich domain, and three potential phosphorylation sites. The human analog of pDIP as characterized by cDNA analysis showed that human DIP (hDIP) differs from the porcine protein in only four residues. Specifically, Arg55 of pDIP is changed to a cysteine in hDIP. Furthermore, hDIP was shown to be present in a large number of tissues by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction/Southern hybridization analysis.
Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptides (DSIP) and Analogs
.png)
Structural models of the Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP) and Analogs
Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP)
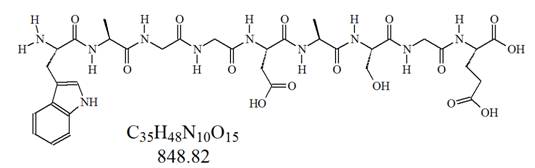

Chemical structure of DSIP


Energy minimized Van-der-Waals model of DSIP using a simple force field modeling approach.
(Asn5)-Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptide
((Asn5)-Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptide (rabbit); (Asn5)-DSIP (rabbit))
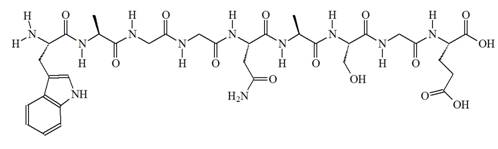

Chemical structure of (Asn5)-DSIP
![Chemical structure of Asn5 DSIP]()
![]()


Energy minimized Van-der-Waals model of (Asn5)-DSIP using a simple force field modeling approach.
(β-Asp5)-Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptide
H-Trp-Ala-Gly-Gly-Asp(Ala-Ser-Gly-Glu-OH)-OH


(β-Asp5)-DSIP: Energy minimized Van-der-Waals model using a simple force field modeling approach.
This peptide analog is a good substrate for protein L-isoaspartyl methyltransferase, an enzyme found in the brain which is involved in the repair of age-damaged proteins containing atypical iosaspartyl peptide bonds.
Porcine Delta-Sleep-Inducing Peptide Immunoreactive Peptide (pDIP)
The solution structure for this peptide was determined by Seidel et al. in 1997.
![Porcine Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide Immunoreactive Peptide pDIP]()
![]()
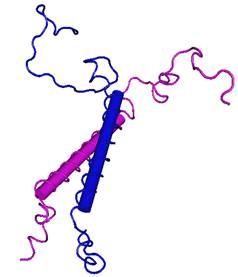

pDIP: Representation of the three-dimensional model of pDIP (Seidel et al 1997).
References
Backmund M, Meyer K, Rothenhaeusler HB and Soyka M (1998). "Opioid detoxification with delta sleep-inducing peptide: results of an open clinical trial.". J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 18: 257–258.
Bjartell A, Ekman R, Sundler F and Widerlöv E (1988). "Delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP): An overview of central actions and possible relationship to psychiatric illnesses". Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 42: 111–117.
Charnay Y, Bouras C, Vallet PG, Golaz J, Guntern R, Constantinidis J (1989). "Immunohistochemical distribution of delta sleep inducing peptide in the rabbit brain and hypophysis". Neuroendocrinology 49: 169–175.
Charnay Y, Golaz J, Vallet PG, Bouras C (1992). "Production and immunohistochemical application of monoclonal antibodies against delta sleep-inducing peptide". J Chem Neuroanat 5: 503–9.
Friedman TC, García-Borreguero D, Hardwick D, Akuete CN, Doppman JL, Dorn LD, Barker CN, Yanovski JA, Chrousos GP (1994). "Decreased Delta-Sleep and Plasma Delta-Sleep-Inducing Peptide in Patients with Cushing Syndrome". Clinical Neuroendocrinology 60: 626–634.
M.V.Graf and A.J.Kastin, Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 8, 83 (1984)1 M. V.Graf and A.J.Kastin, Peptides 7, 1165 (1986)
Graf MV, Kastin AJ.; Delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP): a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1984 Spring;8(1):83-93.
M.V. Graf, G.A. Schoenenberger; DSIP affects adrenergic stimulation of rat pineal N-acetyltransferase in vivo and in vitro. Volume 7, Issue 6, November–December 1986, Pages 1001–1006.
Graf MV, Kastin AJ.; Delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP): an update. Peptides. 1986 Nov-Dec;7(6):1165-87.
Gimble JM, Ptitsyn AA, Goh BC, Hebert T, Yu G, Wu X, Zvonic S, Shi X-M and Floyd ZE (2009). "Delta sleep-inducing peptide and glucocorticoidinduced leucine zipper: potential links between circadian mechanisms and obesity?". Obesity reviews 10: 46–51.
Gupta V, Awasthi N and Wagner BJ (2007). "Specific Activation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Modulation of Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Lens Epithelial Cells". Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 48: 1724–1734.
B.A. Johnson and D.W.Aswad, Neurochem. Res. r8, 87 (1993)
Iyer KS, Marks GA, Kastin AJ, and McCann SM (1988). "Evidence for a role of delta sleep-inducing peptide in slow-wave sleep and sleep-related growth hormone release in the rat". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 3653–3656.
Khvatova EM, Samartzev VN, Zagoskin PP, Prudchenko IA, Mikhaleva II (2003). "Delta sleep inducing peptide (DSIP): effect on respiration activity in rat brain mitochondria and stress protective potency under experimental hypoxia". Peptides 24: 307–311.
Kovalzon VM (1994). "DSIP: a sleep peptide or unknown hypothalamic hormone?". J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 30: 195–199.
Kovalzon VM (2001). "Sleep-Inducing Properties of DSIP Analogs: Structural and Functional Relationships". Biology Bulletin 28: 394–400.
Kovalzon VM, Strekalova TV; Delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP): a still unresolved riddle. J Neurochem. 2006 Apr; 97(2):303-9.
Nakagaki K, Ebihara S, Usui S, Honda Y, Takahashi Y, Kato N (1986). "Effects of intraventricular injection of anti-DSIP serum on sleep in rats". Yakubutsu Seishin Kodo (Japanese journal of psychopharmacology) 6: 259–65.
Nakamura A, Nakashima M, Sugao T, Kanemoto H, Fukumura Y, Shiomi H (1988). "Potent antinociceptive effect of centrally administered delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP)". Eur J Pharmacol 155: 247–53.
Pollard BJ and Pomfrett CJD (2001). "Delta sleep-inducing peptide". Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 18: 419–422.
Pomfrett CJD, Dolling S, Anders NRK, Glover DG, Bryan A, Pollard BJ (2009). "Delta sleep-inducing peptide alters bispectral index, the electroencephalogram and heart rate variability when used as an adjunct to isoflurane anaesthesia". Eur J Anaesthesiol 26: 128–34.
Irina G. Popovich, Boris O. Voitenkov, Vladimir N. Anisimov, Vadim T. Ivanov, Inessa I. Mikhaleva, Mark A. Zabezhinski, Irina N. Alimova, Dmitri A. Baturin a, Natalia Yu. Zavarzina, Svetlana V. Rosenfeld, Anna V. Semenchenko, Anatoli I. Yashin; Effect of delta-sleep inducing peptide-containing preparation Deltaran on biomarkers of aging, life span and spontaneous tumor
incidence in female SHR mice. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 124 (2003) 721-731.
Schneider-Helmert D (1986). "DSIP in Sleep Disturbances". Eur Neurol 25: 154–157.
Schneider-Helmert D and Schoenenberger GA (1981). "The influence of synthetic DSIP (delta-sleep-inducing-peptide) on disturbed human sleep". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 37: 913–917.
Schoenenberger GA, Maier PF, Tobler HJ and Monnier M (1977). "A naturally occurring delta-EEG enhancing nonapeptide in rabbits". European Journal of Physiology 369: 99–109.
Schoenenberger GA (1984). "Characterization, properties and multivariate functions of Delta-Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP)". European Neurology 23: 321–345.
G.A.Schoenenberger and M.Monnier, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 1282 (1977)
Gabi Seidel, Knut Adermann, Thomas Schindler, Andrzej Ejchart, Rainer Jaenicke, Wolf-Georg Forssmann, Paul Roesch; Solution Structure of Porcine Delta Sleep-inducing Peptide Immunoreactive Peptide A Homolog of the Shortsighted Gene Product. THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 272, No. 49, Issue of December 5, pp. 30918–30927, 1997.
Seifritz E, Muller M, Schonenberger G, Trachsel L, Hemmeter U, Hatzinger M, Ernst A, Moore P and Holsboer-Trachsler E (1995). "Human plasma DSIP decreases at the initiation of sleep at different circadian times". Peptides 16: 1475–1481.
Shi X, Shi W, Li Q, Song B, Wan M, Bai S (2003). "A glucocorticoid-induced leucine-zipper protein, GILZ, inhibits adipogenesis of mesenchymal cells". EMBO Rep 4: 374–380.
Sinyukhin AB, Timoshinov GP, Komilov VA, Shabanov PD (2009). "Delta sleep-inducing peptide analogue corrects the eNS functional state of children treated with antiblastomic therapy". European Neuropsychopharmacology 19: S681.
Soyka M and Rothenhaeusler H (1997). "Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide Opioid Detoxification". Am. J. Psychiat. 154: 714–715.
Steiger A and Holsboer F (1997). "Neuropeptides and human sleep". Sleep 20: 1038–1052.
Stanojilovic OP, Zivanovic DP and Su Sic VT (2002). "The effects of Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide on incidence and severity in metaphit-induced epilepsy in rats". Pharmacological Research 45: 241–247.
Stanojlovic OP, Zivanovic DP, Mirkovic S, Mikhaleva II (2004). "Delta sleep-inducing peptide and its tetrapeptide analogue alleviate severity of metaphit seizures". Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 77: 227–234.
Sudakova KV, Umriukhina PE, Rayevskyb KS (2004). "Delta-sleep inducing peptide and neuronal activity after glutamate microiontophoresis: the role of NMDA-receptors". Pathophysiology 11: 81–86.
Sudakova KV, Coghlan JP, Kotov AV, Salieva RM, Polyntsev YV, Koplik EV (1995). "Delta-sleep inducing peptide sequels in mechanisms of resistance to emotional stress". Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 771: 240–251.
Susić V, Masirević G, Totić S (1987). "The effects of delta-sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) on wakefulness and sleep patterns in the cat". Brain Research 414: 262–70.
Walleus H, Widerlöv E and Ekman R (1985). "Decreased concentrations of delta-sleep inducing peptide in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid from depressed patients". Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 39: 63–67.
Westrin A, Ekman R, and Traskman-Bendz L (1998). "High Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide-Like Immunoreactivity in Plasma in Suicidal Patients with Major Depressive Disorder". Biological Psychiatry 43: 734–739.
Yehuda S, Kastin AJ and Coy DH (1980). "Thermoragulatory and locomotor effects of DSIP: paradoxical interaction with d-amphetamine". Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 13: 895–900.
Yehuda S and Mostofsky DI (1984). "Modification of the hypothermic circadian cycles induced by DSIP and melatonin in pinealectomized and hypophysectomised rats". Peptides 5: 495–497.
Yehuda S and Carasso R (1988). "DSIP – a tool for investigating the sleep onset mechanism: a review". International J. Neurosci. 38: 345–353.
Yukhananov RY, Tennila TML, Miroshnichenko II, Kudrina VS, Ushakov AN and Melnik EI (1992). "Ethanol and Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide effects on brain monoamines". Pharmacol. Bio-chem. Behav. 43: 683–687.