Shivarov et al. designed and validated this BNA[NC] probe bead-based assay for the Luminex Lab Scan 200 flow platform to allow for the detection and quantification of somatic mutations in Leukemia!
-.-
How does the assay work?
Primers are designed to allow for the amplification of a DNA sequence fragment that contains the mutated sequence codon. One of the primers is labeled with biotin.
- First, human genomic DNA is extracted from blood.
- The exon 23 of the human DNMT3A gene is amplified using the selected forward and reverse primer.
- To determine the exact sequence the purified and amplified DNA piece can be sequenced using Big Dye terminator cycle-sequencing.
- Next, the exon 23 DNMT3A fragments are amplified from either genomic or plasmic DNA samples using a 5’-biotinylated forward primer.
- Genotyping is performed with the BNA[NC] modified oligonucleotide probes connected to microsphere beads, specific for the wild type or the mutant alleles, by direct hybridization.
- The captured DNA fragment containing biotin on its 5’-end is detected with the help of streptavidin-phycoerythrine (SAPE) in the hybridization buffer using the LabScan200 flow platform from Luminex (USA). For more detail review Shivarov et al. 2014.
The outline of the assay is illustrated in the next figure.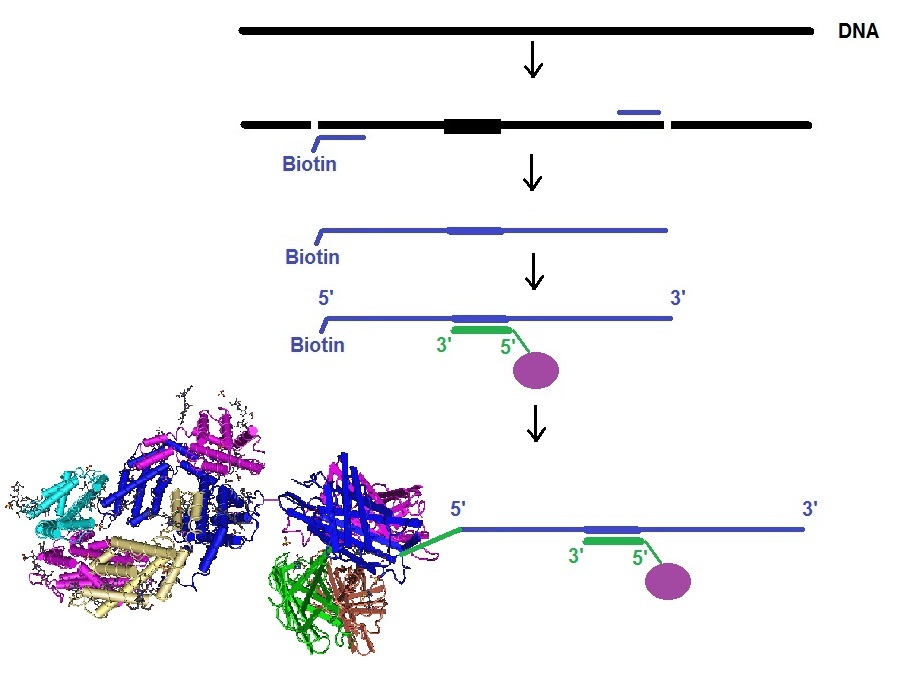
Figure 1: Bead-based suspension assay using BNA [NC] probes to detect and quantify somatic mutations in leukemia. The amplified DNA fragment containing the mutations is captured by the BNA/DNA probes and quantitatively detected with the help of the SAPE complex allowing the analysis in a Luminex system.
Reference
Shivarov V, Ivanova M, Naumova E; Rapid Detection of DNMT3A R882 Mutations in Hematologic Malignancies Using a Novel Bead-Based Suspension Assay with BNA(NC) Probes. PLoS One. 2014 Jun 10;9(6):e99769. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099769. eCollection 2014..png)

















